Computer-aided drug design (CADD) has penetrated into all aspects of drug discovery, and with the in-depth application of artificial intelligence and cloud computing, it is foreseeable that CADD will play a greater role in drug discovery projects in the future, improving efficiency and further reducing high costs of drug development. Creative Biostructure 's CADD and virtual screening platform is a comprehensive platform for new drug discovery that integrates a variety of computer applications. It can be utilized for early preclinical research of small molecule drugs, peptides, antibodies, and therapeutic proteins.
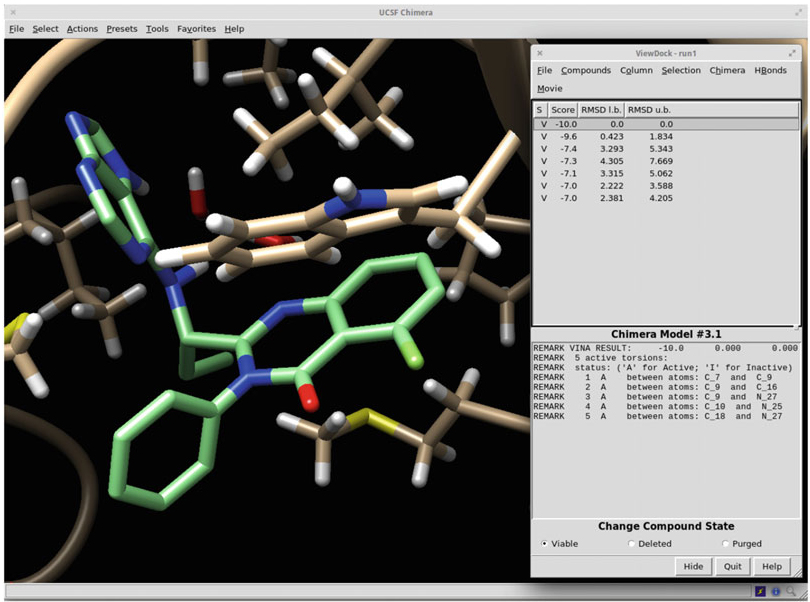 Figure 1. Molecular docking using the UCSF Chimera for AutoDock Vina.
Figure 1. Molecular docking using the UCSF Chimera for AutoDock Vina.
Our MagHelix™ CADD Platform plays a significant role in the virtual screening of active compounds, structural optimization of leads, and computer-aided ADME/T prediction in the process of small molecule drug development. High-performance software enables us to provide highly effective solutions in the field of biopharmaceuticals, such as antibody affinity maturation and antibody humanization design.
| Target Modeling | Homology modeling and Ab initio modeling for building a model for a target whose structure is unknown. |
| Molecular Docking | Prediction of the target-ligand binding mode and approximate binding energy using professional docking software. |
| Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulation | Mainstream MD simulation software and software codes are utilized to gather information about the dynamic properties of targets and docked complexes. |
| Structure-based Virtual Screening (SBVS) | Hit series are screened out from the compound library based on molecular docking and affinity scoring. The screening process can be restricted by MD simulations and pharmacophore modeling. |
| Pharmacophore Modeling | Pharmacophore modeling based on ligands or receptors describes the molecular features necessary for interaction between targets and ligands. |
| Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship (QSAR) Modeling | CoMFA, CoMSIA, and other widely used multi-dimensional QSAR strategies to establish quantitative relationships between chemical structure and biological activity of compounds. |
| Ligand-based Virtual Screening (LBVS) | Hit series are screened out from the compound library based on similarity searching, pharmacophore searching, and QSAR modeling. |
| De Novo Design | Generation of novel molecular structures with desired pharmacological properties based on the target structure or ligand from scratch. |
| Fragment-to-Lead | In silico strategies such as pocket druggability prediction, hot spots analysis, SARs by catalog, and de novo design. |
| Quantum Mechanics (QM) | Force field parameters from Ab initio calculation and QM/MM calculation are utilized to explore binding mechanism details. |
| ADMET Modeling and Prediction | Prediction of various physicochemical properties of compounds, and establish predictive models for drug bioavailability, blood-brain barrier permeability, P450, hERG toxicity, etc . |
| Target Fishing | Discovery of new targets or toxicity of existing active compounds based on reverse molecular docking, pharmacophore searching, and ligand-based similarity searching. |
Hardware : Super high-performance computer clusters with total 58 blades and 716 cores capable of screening more than 1 million compounds in 10 days.
Software Tools : Schrodinger Drug Discovery Suite, DOCK, Modeller, ChemAxon JChem Suite, CCDC, etc.
Databases : Virtual compound database with more than 2 million unique compounds, including ZINC, MDDR, ACD, NCI, etc.
In-House Databases : Drug Information system.
In the era of big data, we apply data fusion and machine learning algorithms to improve virtual screening and structural optimization. Creative Biostructure offers comprehensive CADD services and supports integrated drug R&D projects. We welcome scientists from the pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical industries to use our CADD platform for drug discovery.
Reference
Related Sections

Easy access to products and services you need from our library via powerful searching tools