Given the significant development in mass spectrometry (MS) related software and hardware, some approaches based on mass spectrometry have been used in the drug discovery, for example, non-covalent mass spectrometry (NC-MS, also called native MS, usually using electrospray ionization mass spectrometry, ESI-MS), affinity selection mass spectrometry (AS-MS, also known as size-exclusion chromatography mass spectrometry, SEC-MS), as well as hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry (HDX-MS). Creative Biostructure provides customized MagHelix™ Mass Spectrometry solutions to analyze the protein-ligand complex interactions with clients from biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries dedicated to drug discovery worldwide.
NC-MS can directly detect weak ligands/fragments that bind to specific targets, determine the stoichiometry, specificities, and binding affinities. It can be utilized to identify the ligand binding sites, study binding thermodynamics, and clarify the mechanism of cooperativity. This information is valuable for the identification, characterization, and optimization of hits/leads. However, the target proteins need to remain stable in an ESI-MS suitable buffer and are limited to soluble proteins. Creative Biostructure can apply this rapid, extremely sensitive, low sample consumption, and automatable technology to fragment-based screening (FBS), hit-to-lead, as well as lead optimization.
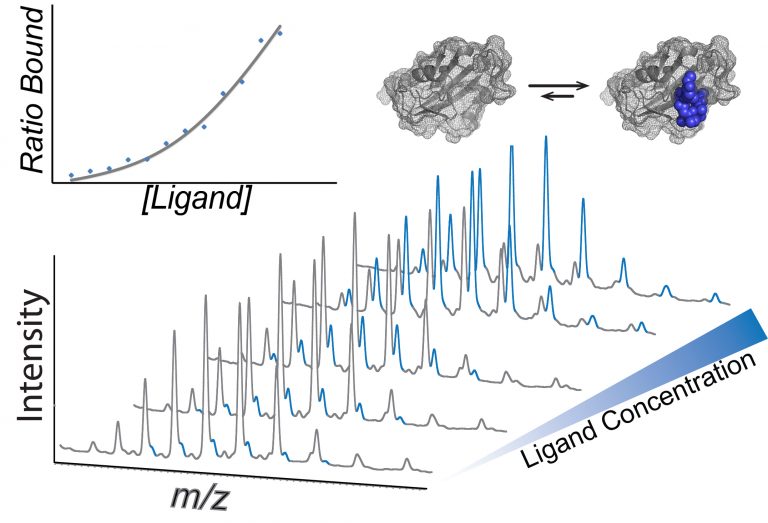 Figure 1. Using NC-MS to inform drug discovery. (Liko I.; et al. 2017)
Figure 1. Using NC-MS to inform drug discovery. (Liko I.; et al. 2017)
We can apply AS-MS technology to the high-throughput screening (HTS) process. The target protein is incubated with a compound library and passed through a size-exclusion chromatography column to separate any compounds bound to the protein and therefore co-elute with the target protein. The protein complexes are dissociated and the ligands are identified by ESI-MS or liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS).
Compared with AS-MS, HDX-MS can provide more information about protein-ligand interactions. The altered accessibility of the deuterium exchange of target protein amino acids involved in ligand binding can be directly measured, thus identifying the binding site and changes in the conformation or dynamics of target protein upon binding. This approach has been successfully utilized to characterize the interaction between antigens and epitopes of corresponding therapeutic antibodies. Whether the target protein is a soluble protein or a membrane-bound protein, and whether it is a small molecule drug or an antibody-based drug, Creative Biostructure can use HDX-MS for further validation and confirmation.
Creative Biostructure has established many biophysical approaches for detecting target-ligand interactions for drug discovery. Each approach operates through different principles and has different strengths and limitations. We can support the individual application of a single technique and can also combine different biophysical approaches into one solution based on project objectives. If you have any related requirements or questions, please feel free to contact us.
References

Easy access to products and services you need from our library via powerful searching tools