Various nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy applications have been developed for the identification and validation of hit compounds and lead optimization. NMR has many advantages, such as the ability to directly observe target proteins and compounds and can be used for protein-based and ligand-based approaches. NMR spectroscopy can also offer significant information about the interactions in the protein-ligand complex, such as structure, affinity, and kinetics, especially in cases where the interactions are too weak to be detected by other approaches or where high-quality crystals of protein-ligand complex cannot be obtained. Among them, the saturation transfer difference (STD) NMR has become a popular ligand-based approach for studying protein-ligand interactions and it has been shown to be particularly effective in fragment screening.
Creative Biostructure applies expertise and experience in NMR spectroscopy technology to lead compound discovery and optimization. We provide STD NMR services to help you directly identify a ligand against the specific target from a mixture of compounds and determine its pharmacophoric groups.
STD NMR experiment involves selective irradiation of proton resonances of proteins using a Gaussian pulse train. Due to the spin-diffusion effect, the saturation spreads rapidly throughout the entire protein. If the ligand binds to the target protein, the saturation will also be transferred to the bound ligand through cross-relaxation at the protein-ligand interface, resulting in a weakening of the ligand signal intensity. The STD spectra containing the bound ligand signals are obtained by subtracting the resulting spectrum from the unsaturated reference spectrum. The approach can provide structural information by distinguishing between solvent-exposed hydrogens and buried hydrogens for the ligand bound to the receptor.
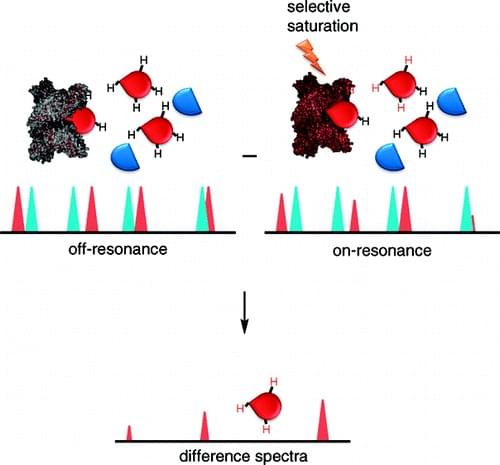 Figure 1. The schematic of saturation transfer difference (STD) NMR. (Viegas A.; et al. 2011)
Figure 1. The schematic of saturation transfer difference (STD) NMR. (Viegas A.; et al. 2011)
Creative Biostructure is confident to provide STD NMR services to assist you in solving ligand screening and binding site characterization in drug discovery programs. Before performing the STD NMR experiment, our scientists will design an experimental strategy according to specific research purposes. Our standard operating procedures ensure the reliability of experimental data. And we will offer all the raw data and analysis reports. Furthermore, a variety of mainstream biophysical techniques for the validation and characterization of hits can be found here.
References

Easy access to products and services you need from our library via powerful searching tools