Microscale thermophoresis (MST) has become a common technique to detect specific target-probe interactions, and it measures the differences in the movement rate through a microscopic temperature gradient caused when complexes are formed. MST can be applied to characterize any type of biomolecular interactions, for example, protein-DNA, protein-RNA, protein-protein, antigen-antibody interactions, as well as the binding of a ligand to ternary complexes.
With the advantages of high sensitivity, low sample consumption, and short experiment time, MST technology is suitable for high-throughput screening (HTS) and fragment-based screening (FBS) in the early stage of drug discovery. Creative Biostructure has been one of the first enterprises to master the latest techniques with forward-looking insights into the development of structure-guided drug discovery. We have established many reliable approaches to meet your drug discovery program requirements. We can provide MST, a relatively new methodology for quantifying biomolecular interactions to assist screen and characterize hit compounds.
MST is a non-immobilized technique for quantitative analysis of biomolecular interactions in solution. The technique is based on thermophoresis and fluorescence detection. The instrument of MST utilizes an infrared laser for local heating to cause molecular directional movement, and then analyze the molecular distribution ratio in the temperature gradient field by fluorescence (fluorescence labeling or intrinsic fluorescence). The MST technique can detect ligand binding-caused changes in thermophoretic mobility, which rely on size, charge, hydration shell, and conformations. Kd values can be estimated using these changes in thermophoretic mobility.
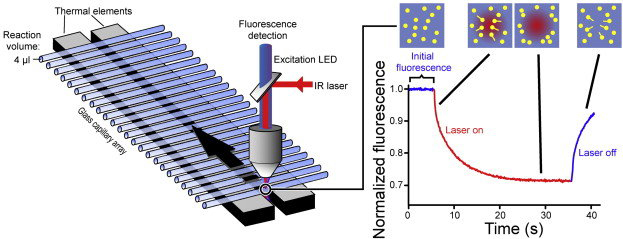 Figure 1. The schematic of MST technology. (Alexander C G.; et al. 2014)
Figure 1. The schematic of MST technology. (Alexander C G.; et al. 2014)
In short, MST has many advantages in the classification and characterization of hits. For example, 1) simple and easy to operate, does not require immobilization and purification of target proteins (fluorescent fusion proteins); 2) Low sample consumption and experimental operation cost; 3) Real-time acquisition of affinity data (such as dissociation constant); 4) This measurement can be performed in a variety of different solutions, including liposomes or detergents needed to study membrane proteins. However, MST depends on the fluorescence of either the compound or the targe, and because the fluorophore itself may affect certain aspects of binding and therefore requires validations.
As an advanced contract service provider in the drug discovery phase, Creative Biostructure can simultaneously apply a variety of established approaches and biophysical techniques to identify, validate, classify and characterize the hit compounds according to the goals and requirements of the project. If your project has such needs, please feel free to contact us, and our scientists will provide professional consultation for you.
References

Easy access to products and services you need from our library via powerful searching tools